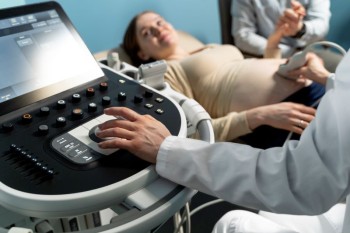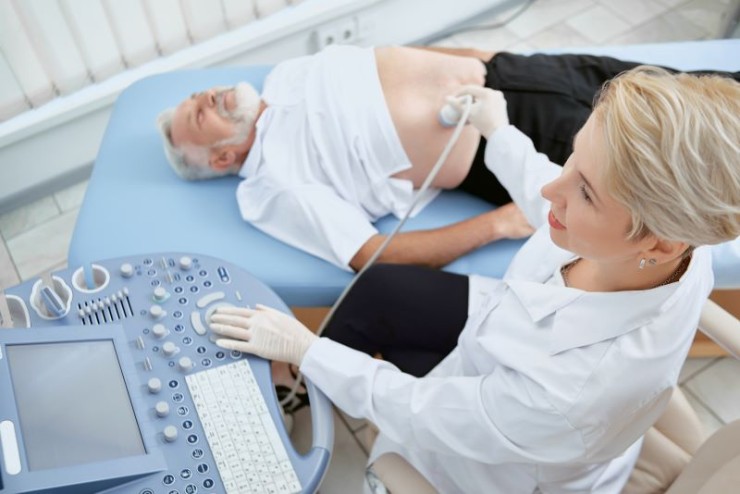
This allows for a comprehensive examination of the liver, gallbladder, kidneys, pancreas, and other abdominal organs.
Ultrasound / USG Whole Abdomen in India with Cost
Ultrasound or USG Whole Abdomen in Detail: Navigating the
Depths of Diagnostic Imaging
In the vast landscape of medical diagnostics, Ultrasound or USG (Ultrasonography) Whole Abdomen stands as a crucial tool, offering a detailed exploration of the internal structures within the abdominal region. This article aims to unravel the intricacies of the procedure, shedding light on its significance, applications, and the valuable insights it provides into abdominal health.
Introduction
Embarking on a journey into the world of Ultrasound or USG Whole Abdomen, we delve into a diagnostic technique that goes beyond the surface. This imaging modality utilizes sound waves to create detailed, real-time images of the organs and structures within the abdominal cavity.
Understanding USG Whole Abdomen
Ultrasound or USG Whole Abdomen is a non-invasive procedure that involves the use of a transducer, which emits high-frequency sound waves. These waves penetrate the abdominal tissues, bouncing back to the transducer to create images on a computer screen. This allows for a comprehensive examination of the liver, gallbladder, kidneys, pancreas, and other abdominal organs.
Importance in Diagnosis
The significance of USG Whole Abdomen lies in its ability to provide a holistic view of abdominal structures. It plays a crucial role in identifying and diagnosing various conditions, including liver disease, gallstones, kidney abnormalities, and abdominal masses.
Preparation for the Scan
Preparing for a USG Whole Abdomen is generally straightforward. Patients are often advised to fast for a few hours before the scan, ensuring a clear visualization of the abdominal organs. Full cooperation with the healthcare provider's instructions enhances the effectiveness of the procedure.
Procedure: A Step-by-Step Guide
Patient Positioning: The patient lies down on an examination table,
often on their back.
Gel
Application: A clear gel is applied to the abdominal area, facilitating
the transmission of sound waves.
Transducer
Movement: The transducer is moved across the abdominal skin,
capturing images of the internal structures.
Real-time
Imaging: The computer screen displays real-time images, allowing the healthcare
provider to examine the organs dynamically.
Imaging Areas
USG Whole Abdomen provides detailed imaging of several vital organs:
Liver: Assessing size, shape, and detecting abnormalities.
Gallbladder: Identifying gallstones and
evaluating gallbladder health.
Pancreas: Examining for inflammation or
tumors.
Kidneys: Assessing size, shape, and
detecting kidney stones.
Spleen: Evaluating size and detecting
abnormalities.
Benefits of USG Whole Abdomen
Non-Invasiveness: Unlike some diagnostic procedures, USG Whole
Abdomen is non-invasive, ensuring patient comfort.
Real-time Imaging: Immediate
visualization of internal structures aids in on-the-spot assessments.
No Radiation Exposure: USG uses sound
waves, eliminating the risks associated with radiation exposure.
Risks and Considerations
USG Whole Abdomen is generally considered safe with minimal risks. The procedure does not involve radiation, making it suitable for various patient populations.
Applications Beyond Routine Imaging
Apart from routine evaluations, USG Whole Abdomen is instrumental in:
Monitoring Chronic Conditions: Regular scans help monitor conditions like
cirrhosis or kidney disease.
Guiding Procedures: Assisting in
procedures such as biopsies or fluid drainage.
Expert Perspectives Medical professionals highlight the versatility of USG Whole Abdomen, emphasizing its role in early detection and monitoring of abdominal conditions. Their insights contribute to its continued significance in healthcare.
Technological Advancements
Ongoing advancements in ultrasound technology, including 3D imaging and elastography, enhance the diagnostic capabilities of USG Whole Abdomen, providing more detailed and nuanced information.
Patient Experience
Patients can expect a painless and quick procedure. The real-time imaging offers an opportunity to discuss findings immediately with the healthcare provider, fostering patient engagement in their healthcare journey.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Ultrasound or USG Whole Abdomen emerges as a pivotal diagnostic tool, offering a detailed exploration of abdominal health. This non-invasive procedure, coupled with real-time imaging and continuous technological advancements, ensures its relevance in the evolving landscape of healthcare.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about USG Whole Abdomen
1. What is the average duration of a USG Whole Abdomen procedure?
On average, the process typically spans a timeframe of 30 to 60 minutes. During this period, the comprehensive imaging of the entire abdominal region allows for a thorough examination of internal structures and facilitates precise diagnostic assessments.
2. Is fasting necessary before the scan?
Fasting is often recommended for a few hours before the scan to ensure optimal visualization.
3. Can USG Whole Abdomen detect cancer?
While it can identify certain abnormalities, further tests may be needed for a conclusive cancer diagnosis.
4. Are there any side effects or risks associated with the procedure?
USG Whole Abdomen is generally safe, with minimal risks or side effects reported.
5. Can pregnant women undergo USG Whole Abdomen?
Yes, ultrasound is considered safe during pregnancy, making USG Whole Abdomen a viable option for assessing abdominal health.
6. Is there any discomfort during the USG Whole Abdomen procedure?
The procedure is generally painless. The gel application and transducer movement may cause mild pressure, but it is well-tolerated by most patients.
7. Can children undergo USG Whole Abdomen?
Yes, children can undergo this procedure, and it is often used to assess abdominal conditions in pediatric patients.
8. How often should someone have a routine USG Whole Abdomen scan?
The frequency of scans depends on individual health factors and any underlying conditions. Your healthcare provider will determine the appropriate schedule for your case.
9. Are there any specific preparations for individuals with dietary restrictions or allergies?
Patients with specific dietary restrictions or allergies should communicate these concerns with their healthcare provider before the scan to ensure appropriate accommodations.
10. Can USG Whole Abdomen detect gastrointestinal issues?
While it primarily focuses on abdominal organs, USG Whole Abdomen can provide insights into certain gastrointestinal issues, such as inflammation or blockages.
11. What happens if abnormalities are detected during the scan?
If abnormalities are detected, further diagnostic tests or medical interventions may be recommended, depending on the nature and severity of the findings.
12. Is USG Whole Abdomen suitable for individuals with obesity?
Yes, USG Whole Abdomen is suitable for individuals with obesity, and it can effectively provide diagnostic information even in patients with higher body mass indexes.
13. Can USG Whole Abdomen be used for emergencysituations?
Yes, USG Whole Abdomen is often used in emergency settings to quickly assess abdominal conditions, such as trauma or acute pain.
14. Is USG Whole Abdomen the same as an abdominal MRI or CT scan?
While all three imaging techniques provide insights into abdominal structures, they differ in terms of the technology used and the information they offer. USG Whole Abdomen does not involve radiation, unlike CT scans.
15. Can USG Whole Abdomen be performed on pregnant women?
Yes, USG Whole Abdomen is considered safe during pregnancy and is often used to assess the health of abdominal organs in pregnant individuals.
These additional FAQs aim to provide a more comprehensive understanding of USG Whole Abdomen, addressing various concerns that individuals may have before undergoing the procedure. Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized information based on your health condition and medical history.
(0)
Login to continue