₹2,800
₹3,500
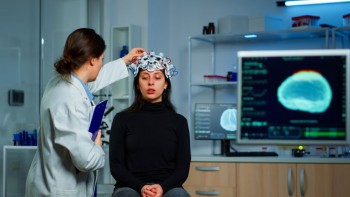
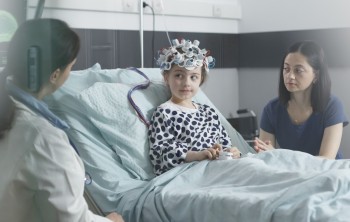
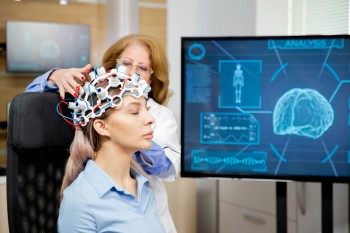
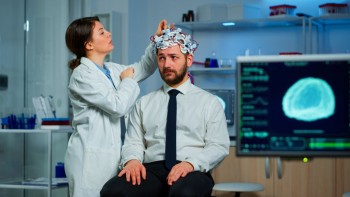
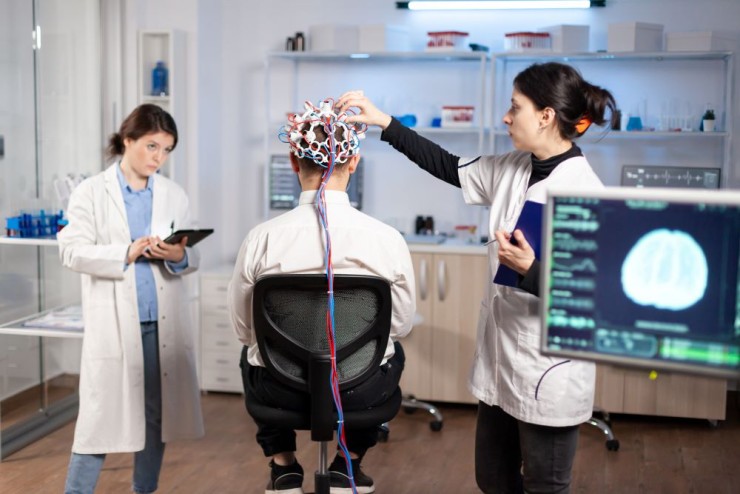
An Electroencephalogram, or EEG, is a medical test that measures the electrical activity in your brain.
Category:
EEG