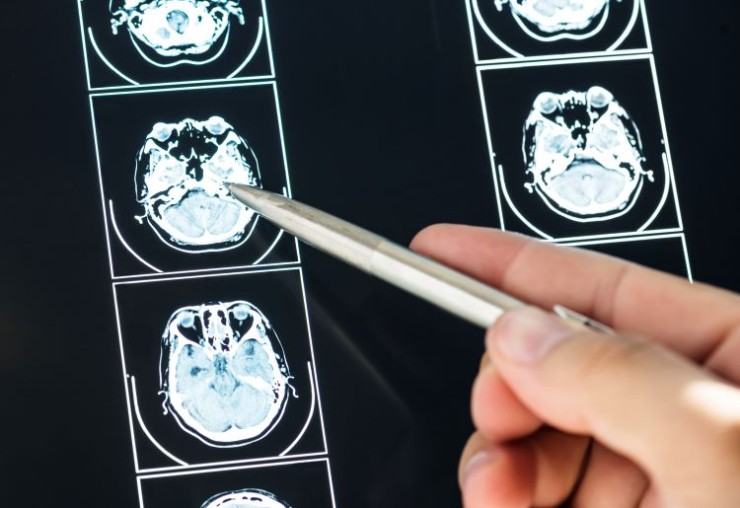
CT Scan Brain Plain is crucial for assessing the structures of the brain, including the skull, ventricles, and brain tissue.
CT Brain Plain in India with Cost
CT Scan Brain Plain in
Detail
Introduction
CT Scan Brain Plain is a diagnostic imaging technique that produces detailed images of the brain without utilizing contrast material. In this article, we delve into the specifics of this imaging technique, its purposes, and how it aids in diagnosing and managing various brain-related conditions.
Purpose and Significance of CT Scan Brain Plain
CT Scan Brain Plain is crucial for assessing the structures of the brain, including the skull, ventricles, and brain tissue. It is commonly used to identify abnormalities such as tumors, bleeding, fractures, and other conditions affecting the brain.
When is a CT Scan Brain
Plain Recommended?
A CT Scan Brain Plain is recommended when a detailed evaluation of the brain structures is necessary, and the use of contrast material is not required. It is often employed for cases of head trauma, suspected bleeding, and routine screening for certain brain conditions.
Preparation for CT Scan Brain Plain
Preparation for a CT Scan Brain Plain is minimal. Patients are usually advised to remove any metal objects or jewelry from the head area, and they should inform the healthcare provider about any existing health conditions or medications.
Procedure of CT Scan Brain Plain
During the procedure, patients lie on a specialized table that moves through the CT scanner. The scanner captures detailed cross-sectional images of the brain, providing a comprehensive view without the use of contrast material.
Benefits and Risks
CT Scan Brain Plain offers high-resolution images, aiding in the accurate diagnosis of various brain conditions. As it does not involve the use of contrast material, the procedure is generally considered safe. The benefits often outweigh the risks, making it a valuable tool in assessing brain health.
Interpreting CT Scan Brain Plain Results
Expertise is crucial in interpreting the results of a CT Scan Brain Plain. Radiologists analyze the images to identify abnormalities, such as tumors, bleeding, fractures, and other conditions affecting the brain. The detailed information obtained guides treatment decisions.
Conditions Diagnosed Through CT Scan Brain Plain
CT Scan Brain Plain is effective in diagnosing a range of conditions, including traumatic brain injuries, intracranial bleeding, tumors, and abnormalities in the brain structures. The detailed images allow for precise identification and characterization of these issues.
Alternatives to CT Scan Brain Plain
While CT Scan Brain Plain is a powerful diagnostic tool, alternative imaging methods like MRI or contrast-enhanced CT may be considered based on the specific clinical scenario. Each method has its strengths and limitations, and the choice depends on the information needed for an accurate diagnosis.
Conclusion
In conclusion, CT Scan Brain Plain is a valuable diagnostic tool for assessing brain structures and identifying various conditions affecting the brain. The detailed images it provides play a crucial role in guiding healthcare professionals toward accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plans.
Frequently Asked Questions About CT Scan Brain Plain
1. What is a CT Scan Brain Plain?
A CT Scan Brain Plain is a diagnostic imaging procedure that provides detailed images of the brain without the use of contrast material. It allows for the assessment of brain structures, including the skull, ventricles, and brain tissue.
2. How long does the procedure take?
The duration of a CT Scan Brain Plain is relatively short, typically taking around 10 to 15 minutes, making it a quick and efficient imaging technique.
3. Is there any discomfort during the procedure?
The procedure is generally well-tolerated, and there is no discomfort associated with the scan itself. Patients may need to remain still during the procedure to ensure clear images.
4. Are there risks associated with CT Scan Brain Plain?
CT Scan Brain Plain is considered safe, and there are minimal risks associated with the procedure. As it does not involve the use of contrast material, allergic reactions are rare.
5. Can pregnant women undergo a CT Scan Brain Plain?
While the radiation exposure is minimal, pregnant women are generally advised to avoid unnecessary imaging procedures. Alternative methods that do not involve ionizing radiation may be considered, and consultation with healthcare providers is crucial.
6. Can a CT Scan Brain Plain detect all types of brain tumors?
CT Scan Brain Plain is effective in detecting certain types of brain tumors, especially those that cause changes in brain structures. However, for more detailed information about specific tumor characteristics, additional imaging methods like contrast-enhanced MRI may be recommended.
7. Is sedation required for children undergoing a CT Scan Brain Plain?
In most cases, sedation is not required for children undergoing a CT Scan Brain Plain. The procedure is relatively quick, and children are usually able to stay still during the scan. However, in specific cases or for very young children, sedation may be considered.
8. Can CT Scan Brain Plain identify the cause of headaches?
CT Scan Brain Plain can identify certain causes of headaches, such as structural abnormalities, bleeding, or tumors. However, it may not always reveal the underlying cause of all types of headaches. Additional evaluations and discussions with healthcare providers are crucial for a comprehensive assessment.
9. How often can one undergo a CT Scan Brain Plain?
The frequency of CT Scan Brain Plain depends on the specific medical condition and the recommendation of healthcare providers. It is generally not advisable to undergo unnecessary imaging, and the decision for repeat scans is made based on the patient's medical history and ongoing symptoms.
10. Is there any age limit for individuals undergoing a CT Scan Brain Plain?
There is no strict age limit for CT Scan Brain Plain. The procedure is performed based on clinical necessity, and healthcare providers assess the potential benefits against the risks, taking into consideration the patient's overall health.
11. Can CT Scan Brain Plain detect neurological conditions like multiple sclerosis?
CT Scan Brain Plain is not the primary imaging method for detecting conditions like multiple sclerosis. More advanced imaging techniques such as MRI with specific sequences are preferred for assessing neurological conditions, providing detailed information about the brain's soft tissues.
12. Are there any side effects after undergoing a CT Scan Brain Plain?
Generally, there are no specific side effects after undergoing a CT Scan Brain Plain. Some patients may experience a metallic taste in the mouth if contrast material is used, but this is temporary. Any concerns or unusual symptoms should be promptly reported to healthcare providers.
13. Can CT Scan Brain Plain identify the cause of memory loss?
CT Scan Brain Plain can help identify structural abnormalities in the brain that may contribute to memory loss, such as tumors or bleeding. However, for a comprehensive evaluation of memory-related issues, additional assessments, including neuropsychological testing, may be necessary.
14. Is there a difference between CT Scan Brain Plain and CT Scan Brain with Contrast?
The primary difference is the use of contrast material. CT Scan Brain Plain provides images without contrast, while CT Scan Brain with Contrast involves the injection of contrast material to enhance certain structures' visibility. The choice depends on the diagnostic needs and clinical considerations.
15. Can individuals with claustrophobia undergo a CT Scan Brain Plain?
Yes, individuals with claustrophobia can typically undergo a CT Scan Brain Plain comfortably. Unlike MRI, CT scanners are open, and the procedure is brief, reducing the likelihood of discomfort for individuals with claustrophobia.
These FAQs provide additional insights into various aspects of CT Scan Brain Plain, addressing common concerns and considerations. Always consult with healthcare professionals for personalized information based on individual health circumstances.
(0)
Login to continue