₹9,999
₹13,700
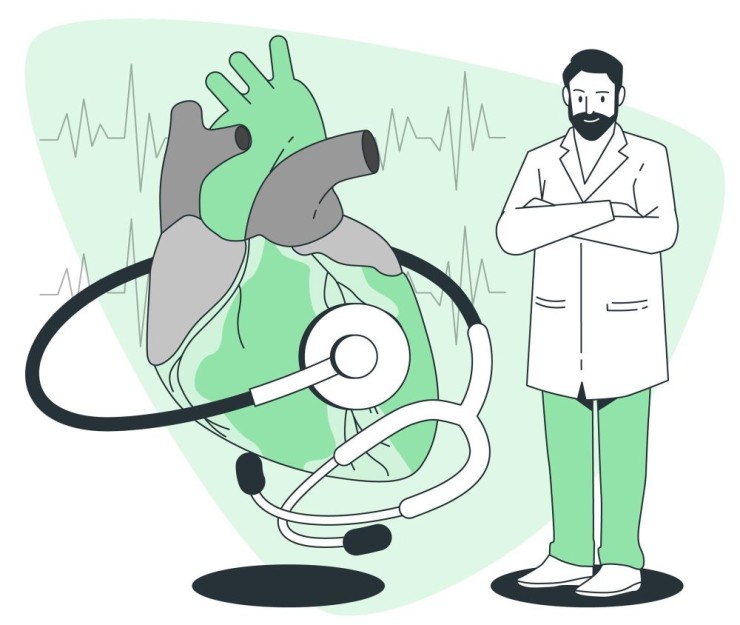
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) is a state-of-the-art medical imaging technique that offers unparalleled insights into the intricacies of the heart's structure and function.
Category:
MRI Scan